Smarter AI Inference Routing on Kubernetes with Gateway API Inference Extension
Christian Posta
Mar 25, 2025
The kgateway 2.0 release includes support for the new Kubernetes Gateway API Inference Extension. This extension brings AI/LLM awareness to Kubernetes networking, enabling organizations to optimize load balancing and routing for AI inference workloads. This post explores why this capability is critical and how it improves efficiency when running AI workloads on Kubernetes.
Enterprise AI and Kubernetes
As organizations increasingly adopt LLMs and AI-powered applications, many choose to run models within their own infrastructure due to concerns around data privacy, compliance, security, and ownership. Sensitive data should not be sent to external / hosted LLM providers. Instrumenting with RAG, model fine tuning, etc that may allow sensitive data to leak (or potentially be used for training for the model provider) may be best done in-house.
Kubernetes has become the go-to infrastructure for deploying AI models due to its flexibility, scalability, and deep integration with GPUs. GPUs are expensive resources, and Kubernetes offers multiple mechanisms to optimize their usage, including time slicing, Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) partitioning, virtual GPUs, and NVIDIA MPS for concurrent processing.
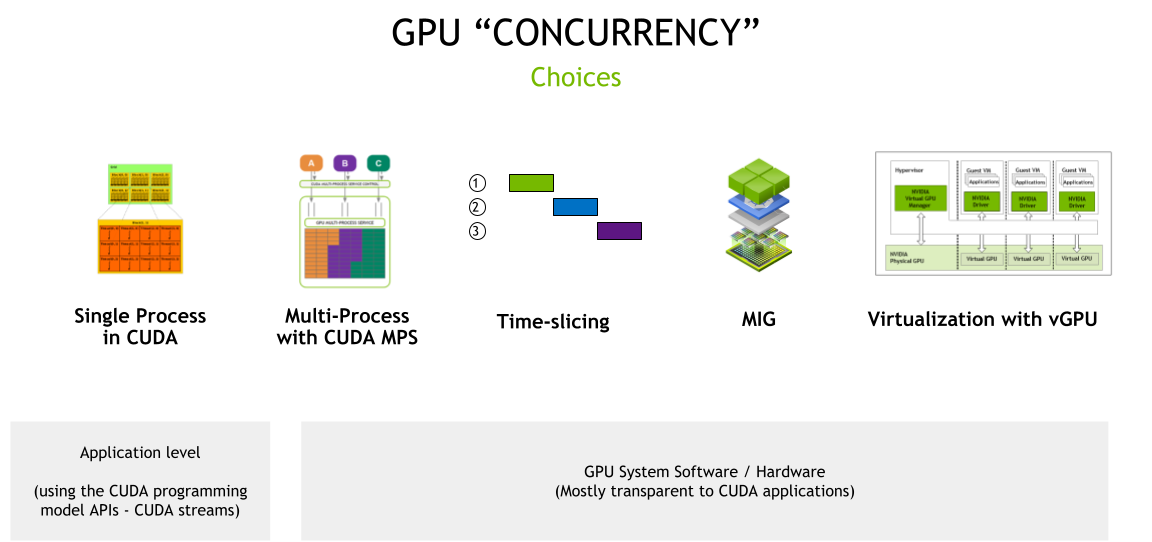
While much of the focus has been on backend optimizations to maximize GPU efficiency, effective utilization isn’t just about hardware allocation; it also depends on how inference requests are routed and load-balanced across model-serving instances. Simple load-balancing strategies often fall short in handling AI workloads effectively, leading to suboptimal GPU usage and increased latency.
The Challenge of Routing AI Inference Traffic
Unlike traditional web traffic, AI inference requests have unique characteristics that make conventional load-balancing techniques less effective. Inference requests often take much longer to process, sometimes several seconds (or even minutes!) rather than milliseconds, and involve significantly larger payloads (ie, with RAG, multi-turn chats, etc). A single request can consume an entire GPU, making scheduling decisions far more impactful than those for standard API workloads. At times these requests need to queue up while others are being processed.
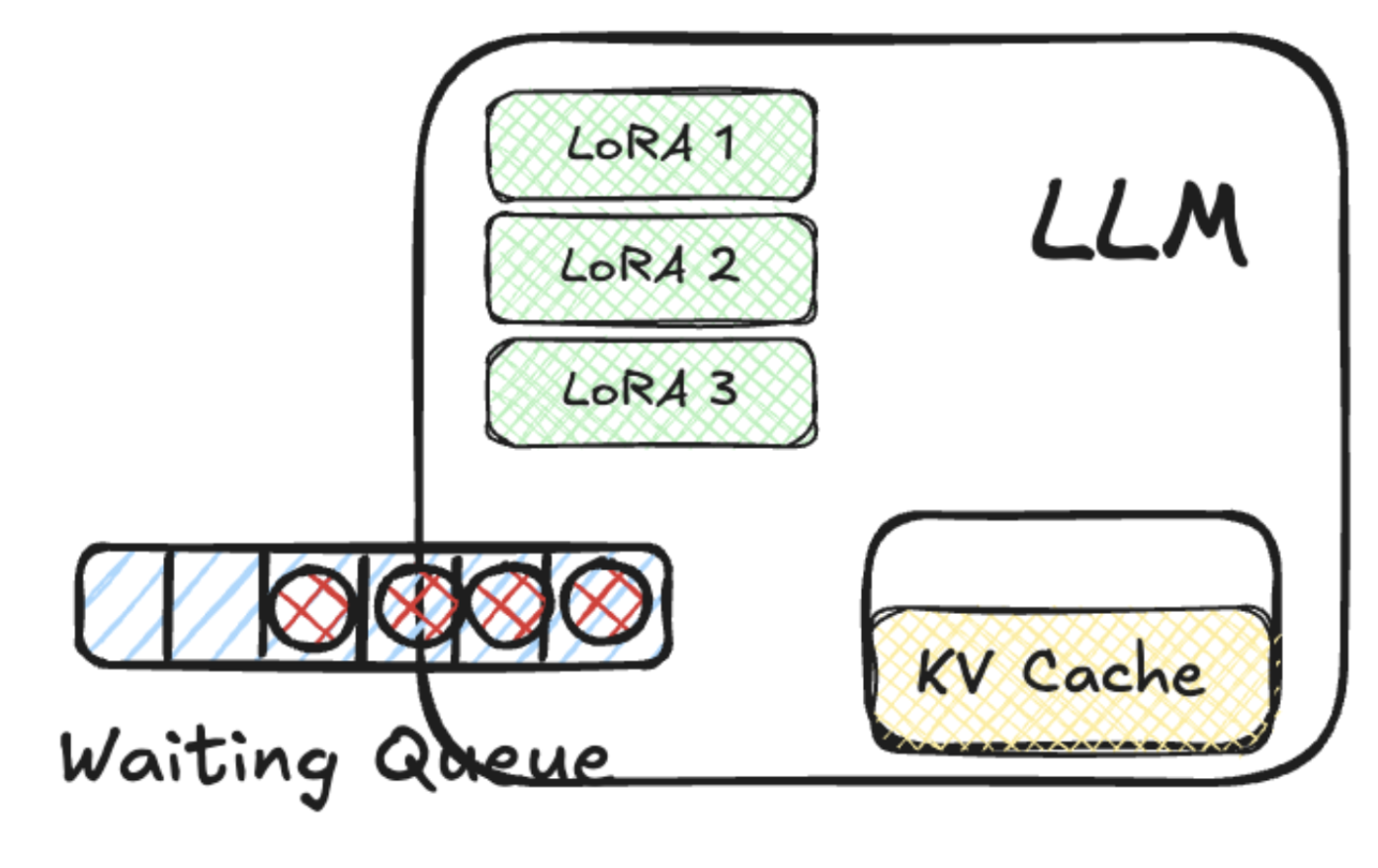
Another key consideration is that AI models often maintain in-memory caches, such as KV storage for prompt tokens, which help improve performance. Some models also load fine-tuned adapters, like LoRA, to customize responses based on specific user or organization needs. Routing decisions need to account for these “stateful” nuances—requests should not only be distributed evenly but should also be directed to instances that are best suited to handle them based on their current state, available memory, and request queue depth.
Introducing the Gateway API Inference Extension
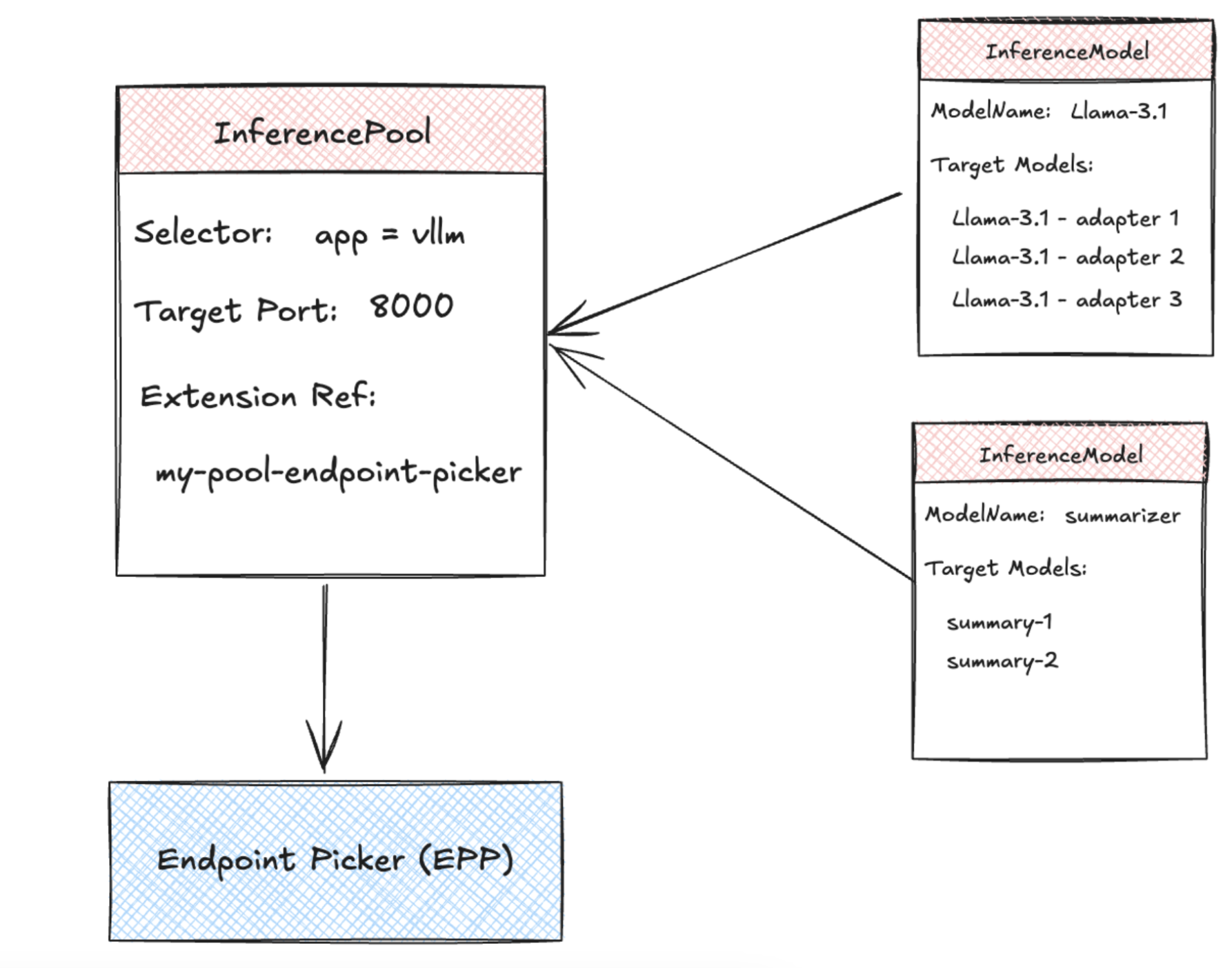
To address these challenges, the Kubernetes Gateway API Inference Extension introduces inference-aware routing through two new Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs): InferenceModel and InferencePool.
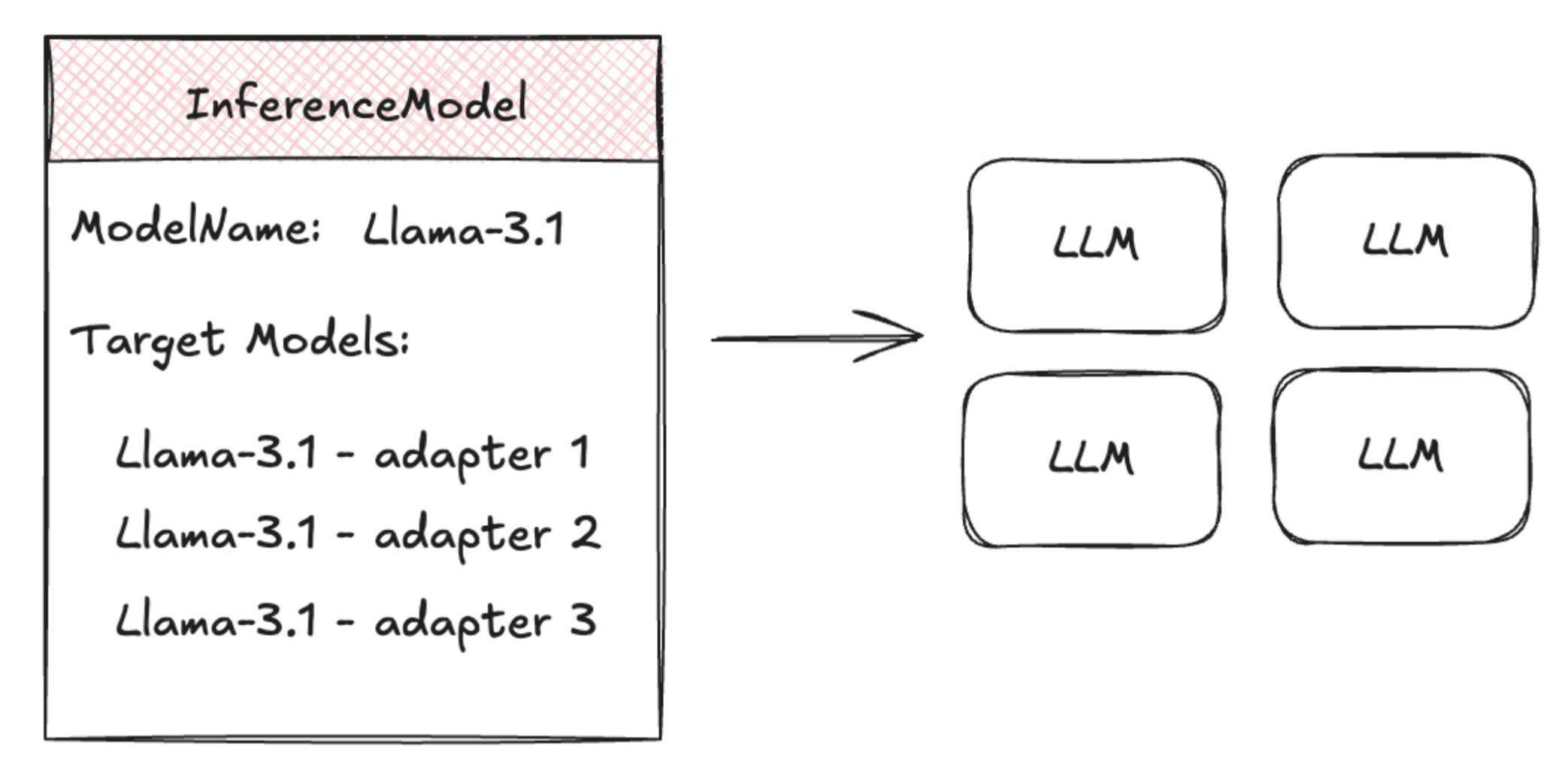
The InferenceModel CRD is designed for AI engineers, allowing them to define logical model endpoints. It maps user-facing model names to backend models and provides flexibility for traffic splitting between fine-tuned adapters. Additionally, it enables workload owners to specify request criticality, ensuring that real-time services receive priority over best-effort batch jobs.
The InferencePool CRD, on the other hand, is intended for platform operators managing model-serving infrastructure. It represents a group of model-serving instances and acts as a specialized backend service for AI workloads. The pool manages inference-aware endpoint selection, making intelligent routing decisions based on real-time metrics such as request queue depth and GPU memory availability.
How Inference Routing Works in kgateway
When a request reaches the kgateway, it will follow typical Gateway API HTTPRoute policy to determine which backend should handle the request. The backend in this case is an InferencePool:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: llm-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
name: inference-gateway
sectionName: llm-gw
rules:
- backendRefs:
- group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io
kind: InferencePool
name: my-pool
port: 8000
weight: 1
matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
timeouts:
backendRequest: 24h
request: 24hInstead of forwarding the request to an Envoy upstream cluster (which happens for typical API services), the Gateway invokes an inference-aware endpoint selection extension. This extension evaluates the live state of model-serving instances by watching prometheus metrics, considering factors such as LLM queue depth, available GPU memory, and whether the required adapters are preloaded. Based on these real-time metrics, it selects the most optimal model server pod for the request, ensuring better resource utilization and lower latency. Once a routing decision is made, the request is forwarded to the chosen pod, and the response is streamed back to the client.
This approach ensures that requests to AI/LLM models are distributed efficiently across available GPUs, preventing overload on specific instances while maximizing overall system performance. By introducing inference-aware logic into the routing layer, Kubernetes can optimize both latency and GPU utilization far beyond what traditional load-balancing or scheduling techniques allow.
Deploying Inference Extension in kgateway
You can deploy kgateway with inference extension enabled with the following helm configuration:
helm upgrade -i --namespace kgateway-system --version v2.0.0 kgateway
oci://cr.kgateway.dev/kgateway-dev/charts/kgateway
--set inferenceExtension.enabled=trueYou’ll also need the inference extension CRDs deployed to your cluster:
kubectl apply -f
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api-inference-extension/releases/download/${INF_EXT_VERSION}/manifests.yamlTo configure Gateway API Inference Extension with kgateway, you can specify an InferenceModel such as the following:
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2
kind: InferenceModel
metadata:
name: inferencemodel-sample
spec:
criticality: Critical
modelName: tweet-summary
poolRef:
group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io
kind: InferencePool
name: my-pool
targetModels:
- name: tweet-summary-0
weight: 50
- name: tweet-summary-1
weight: 50In this InferenceModel, we specify a client-facing model name tweet-summary that we then split across multiple backend LLM LoRA adapters tweet-summary-0' 'tweet-summary-1. This mechanism can be used to introduce new fine-tuned adapters or run blue-green or canary releases of model changes. Notice also that a criticality level can be set. This can affect how requests get treated when the backend LLMs are under load: critical requests will attempt to be load-balanced, while sheddable requests may be dropped.
We also need to specify an InferencePool which will act as our Gateway API backend to which we can route:
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2
kind: InferencePool
metadata:
name: my-pool
spec:
targetPortNumber: 8000
selector:
app: vllm-<modelname>
extensionRef:
name: my-pool-endpoint-pickerThis resource is similar to a Kubernetes service in that it specifies a selector and target port for the backend LLM (ie, InferenceModel endpoints) The InferencePool resource specifies an endpoint picker (EPP) in the extensionRef field. In kgateway, you specify a name that is <pool-name>-endpoint-picker.
So if your InferencePool is named my-pool you would use extensionRef: my-pool-endpoint-picker. This endpoint picker component gets spun up automatically and this is what handles the model-based load balancing.
Conclusion
AI workloads on Kubernetes demand more than basic HTTP routing—LLMs require intelligent traffic management to ensure optimal performance. The Gateway API Inference Extension introduces model-aware, GPU-efficient load balancing, bringing significant improvements in resource utilization and response times.
By leveraging this extension, organizations can leverage smarter AI traffic routing in their Kubernetes environments, ensuring that GPU infrastructure is used as effectively as possible. With kgateway’s support for Gateway API inference extension, developers and platform operators alike can take advantage of these capabilities to streamline AI workloads.
Try kgateway in our free hands-on labs, get involved in the community, and give us feedback for how we can improve!
Acknowledgements: Thanks to Daneyon Hansen (Solo.io) for his work on getting Gateway Inference Extension into kgateway, and to the whole community of Inference Extension maintainers!