Dynamic MCP
Route to a dynamic Model Context Protocol (MCP) server by using a label selector. For more information, see the About MCP topic.
Before you begin
-
Follow the Get started guide to install kgateway with agentgateway enabled.
-
Make sure that agentgateway is enabled in kgateway.
helm get values kgateway -n kgateway-system -o yamlExample output:
agentgateway: enabled: true
Step 1: Deploy an MCP server
Deploy an MCP server that you want agentgateway to proxy traffic to. The following example sets up an MCP server that provides various utility tools.
-
Create an MCP server (
mcp-server) that provides various utility tools. Notice that the Service uses theappProtocol: kgateway.dev/mcpsetting. This way, kgateway configures the agentgateway proxy to use MCP for the Backend that you create in the next step.kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: mcp-server-everything labels: app: mcp-server-everything spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: mcp-server-everything template: metadata: labels: app: mcp-server-everything spec: containers: - name: mcp-server-everything image: node:20-alpine command: ["npx"] args: ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-everything", "streamableHttp"] ports: - containerPort: 3001 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: mcp-server-everything labels: app: mcp-server-everything spec: selector: app: mcp-server-everything ports: - protocol: TCP port: 3001 targetPort: 3001 appProtocol: kgateway.dev/mcp type: ClusterIP EOF -
Create a Backend for your MCP server that uses label selectors to select the MCP server.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1 kind: Backend metadata: name: mcp-backend spec: type: MCP mcp: name: mcp-virtual-server targets: - selectors: serviceSelector: matchLabels: app: mcp-server-everything EOF
Step 2: Route with agentgateway
Route to the MCP server with agentgateway.
-
Create a Gateway resource that uses the
agentgatewayGatewayClass. Kgateway automatically creates an agentgateway proxy for you.kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Gateway metadata: name: agentgateway spec: gatewayClassName: agentgateway listeners: - protocol: HTTP port: 8080 name: http allowedRoutes: namespaces: from: All EOF -
Verify that the Gateway is created successfully. You can also review the external address that is assigned to the Gateway. Note that depending on your environment it might take a few minutes for the load balancer service to be assigned an external address. If you are using a local Kind cluster without a load balancer such as
metallb, you might not have an external address.kubectl get gateway agentgatewayExample output:
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE agentgateway agentgateway 1234567890.us-east-2.elb.amazonaws.com True 93s -
Create an HTTPRoute resource that routes to the Backend that you created in the previous step.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: HTTPRoute metadata: name: mcp labels: example: mcp-route spec: parentRefs: - name: agentgateway namespace: default rules: - backendRefs: - name: mcp-backend group: gateway.kgateway.dev kind: Backend EOF
Step 3: Verify the connection
Use the MCP Inspector tool to verify that you can connect to your MCP server through agentgateway.
-
Get the agentgateway address.
export INGRESS_GW_ADDRESS=$(kubectl get gateway agentgateway -o=jsonpath="{.status.addresses[0].value}") echo $INGRESS_GW_ADDRESSkubectl port-forward deployment/agentgateway 8080:8080 -
From the terminal, run the MCP Inspector command. Then, the MCP Inspector opens in your browser.
npx modelcontextprotocol/inspector#0.16.2 -
From the MCP Inspector menu, connect to your agentgateway address as follows:
- Transport Type: Select
Streamable HTTP. - URL: Enter the agentgateway address and the
/mcppath, such as${INGRESS_GW_ADDRESS}/mcporhttp://localhost:8080/mcp. - Click Connect.
- Transport Type: Select
-
From the menu bar, click the Tools tab, then click List Tools.
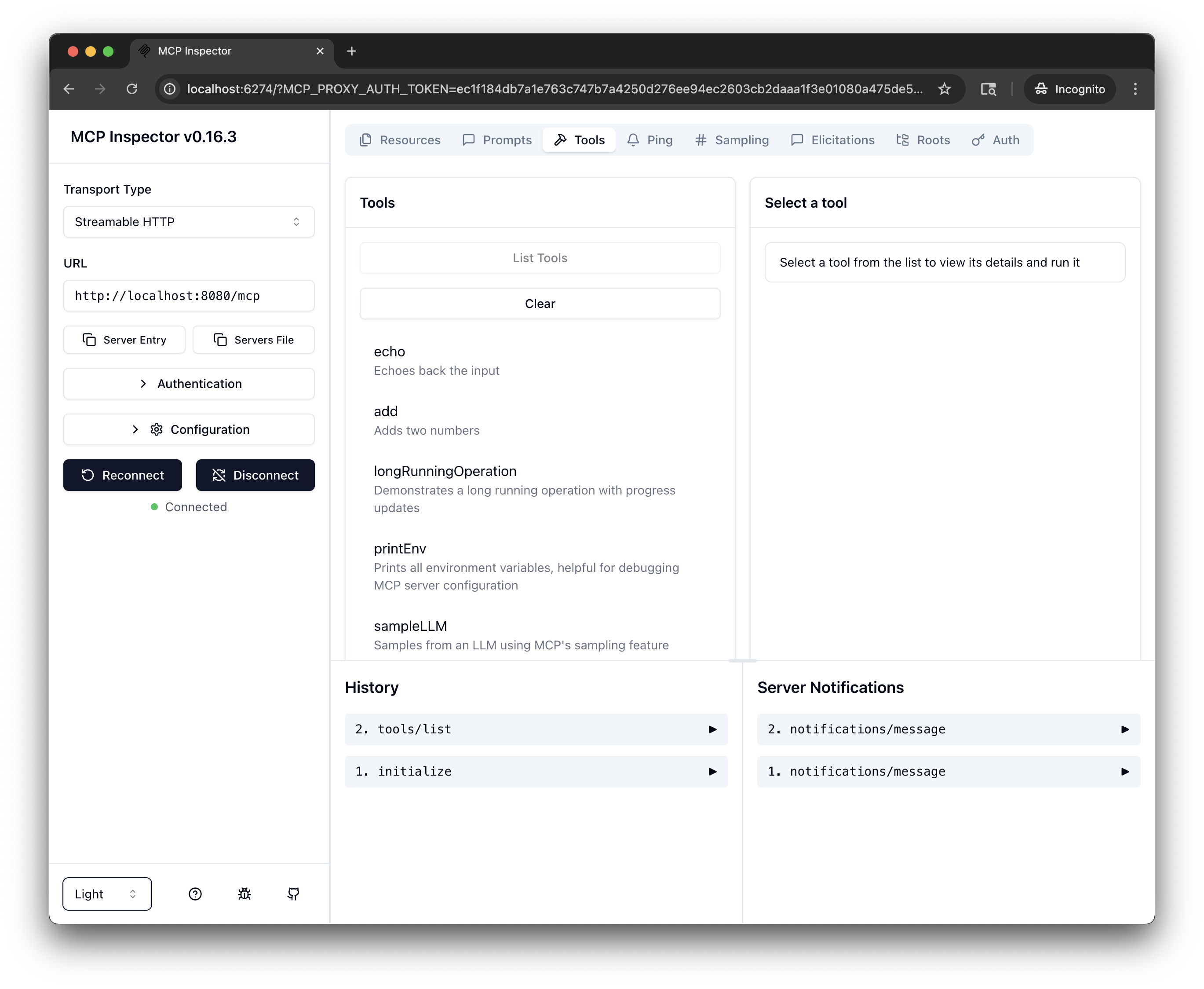
-
Test the tools: Select a tool, such as
echo. In the message field, enter a message, such asHello, world!, and click Run Tool.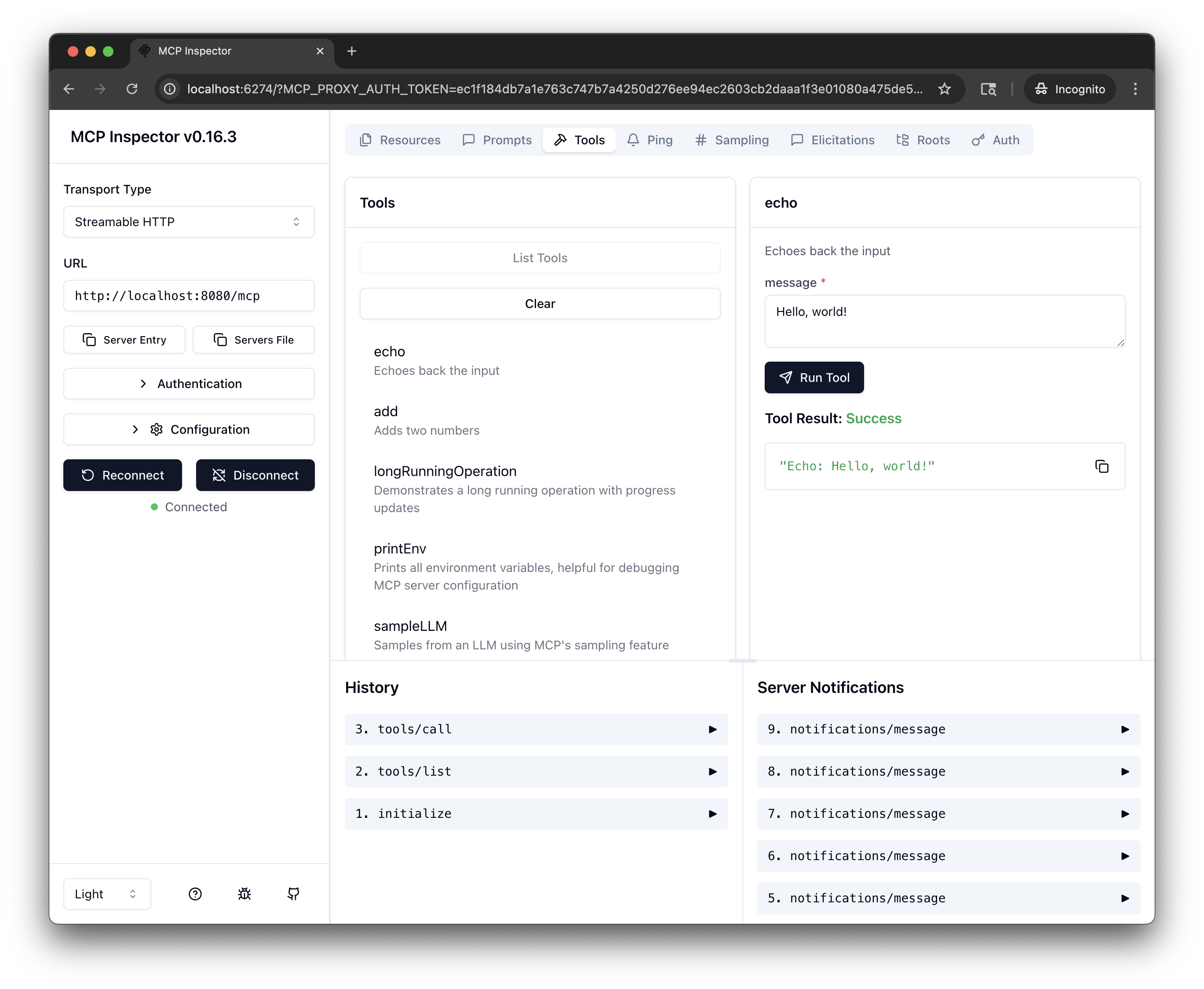
Cleanup
You can remove the resources that you created in this guide.kubectl delete Deployment mcp-server-everything
kubectl delete Service mcp-server-everything
kubectl delete Backend mcp-backend
kubectl delete Gateway agentgateway
kubectl delete HTTPRoute mcp